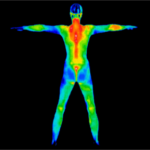
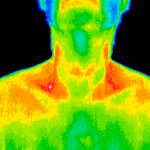
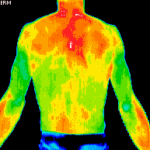
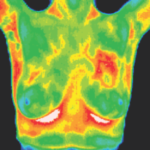
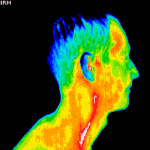
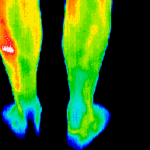
Digital Infrared Thermal Imaging (DITI or Thermography) is used for detecting muscular/skeletal, vascular and nervous system irregularities, compensatory issues, stroke and inflammation screening, monitoring injury or chronic disease and much more.
Full Body Imaging includes 22-28 views from head to toe.
Upper Body Imaging includes 18-22 views from pubic bone to head.
(Female patients: breast study is included with Upper Body or Full Body Thermography at no additional charge).
Click here to see details and pricing for thermography in Naples at Be Well Thermal Imaging's clinic.
This safe, affordable full body study can aid in...
- communicating complaints
- detecting compensatory problems
- demonstrating physiological changes in injury or chronic disease
Thermal abnormalities are present in many diseases and physical injuries. Digital Infrared Thermal Imaging (DITI) can help doctors and clinicians diagnose, evaluate, monitor and document a large number of injuries and conditions, including soft tissue injuries, sensory/autonomic nerve fibre dysfunction, chronic inflammation, and more. Also known as Thermography, it is used as an aid for diagnosis and prognosis, as well as therapy follow up and rehabilitation monitoring, within clinical fields that include rheumatology, neurology, physiotherapy, sports medicine, oncology, pediatrics, orthopedics and many others.
Thermography's major clinical value is in its high sensitivity to pathology in the vascular, muscular, neural and skeletal systems. It can show a combined effect of the autonomic nervous system and the vascular system, down to capillary dysfunctions. The effects of these changes show as asymmetries in temperature distribution on the surface of the body. Vascular conditions are readily demonstrated including raynauds, vasculitis, limb ischemia, DVT, etc.
Clinical applications for Medical Digital Infrared Thermal Imaging include:
- To define the extent of a lesion of which a diagnosis has previously been made
- To localise an abnormal area not previously identified, so further diagnostic tests can be performed
- To detect early lesions before they are clinically evident
- To monitor the healing process before the patient is returned to work or training
Medical DITI is filling the gap in clinical diagnosis ...
- X-ray, CT, Ultrasound and MRI are tests of anatomy
- EMG is a test of motor physiology
- DITI is unique in its capability to show physiological change and metabolic processes. It has also proven to be a very useful complementary procedure to other diagnostic modalities.
- Medical DITI is non-invasive. There is no contact, no radiation and no use of contrast agents.
- Medical DITI can offer considerable financial savings by avoiding the need for more expensive investigations.
Results obtained with medical DITI systems are totally objective and show excellent correlation with other diagnostic tests.
Medical DITI is a noninvasive diagnostic technique that allows the examiner to visualise and quantify changes in skin surface temperature. An infrared scanning device is used to convert infrared radiation emitted from the skin surface into electrical impulses that are visualised in colour on a monitor. This visual image graphically maps the body temperature and is referred to as a thermogram. The spectrum of colours indicate an increase or decrease in the amount of infrared radiation being emitted from the body surface. Since there is a high degree of thermal symmetry in the normal body, subtle abnormal temperature asymmetry's can be easily identified.
The neuro-thermography application of DITI measures the somatic component of the sympathetic nervous system by assessing dermal blood flow. The sympathetic nervous system is stimulated at the same anatomical location as its sensory counterpart and produces a 'somato sympathetic response'. The somato sympathetic response appears on DITI as a localised area of altered temperature with specific features for each anatomical lesion.
The mean temperature differential in peripheral nerve injury is 1.5°C. In sympathetic dysfunction's (RSD / SMP / CRPS) temperature differentials ranging from 1° C to 10° C depending on severity are not uncommon. Rheumatological processes generally appear as 'hot areas' with increased temperature patterns. The pathology is generally an inflammatory process, i.e. synovitis of joints and tendon sheaths, epicondylitis, capsular and muscle injuries, etc.
Both hot and cold responses may co exist if the pain associated with an inflammatory focus excites an increase in sympathetic activity. Also, vascular conditions are readily demonstrated by DITI including Raynauds, Vasculitis, Limb Ischemia, DVT, etc.
How to Prepare
Please click here for instructions on how to prepare for your thermography appointment.
BOOK AN APPOINTMENT
Click here to schedule thermography in Naples via the Be Well Thermal Imaging appointment tool.






